
If your business is registered for GST, you calculate your deduction differently because you claim the GST component of the expense in your business activity statement.
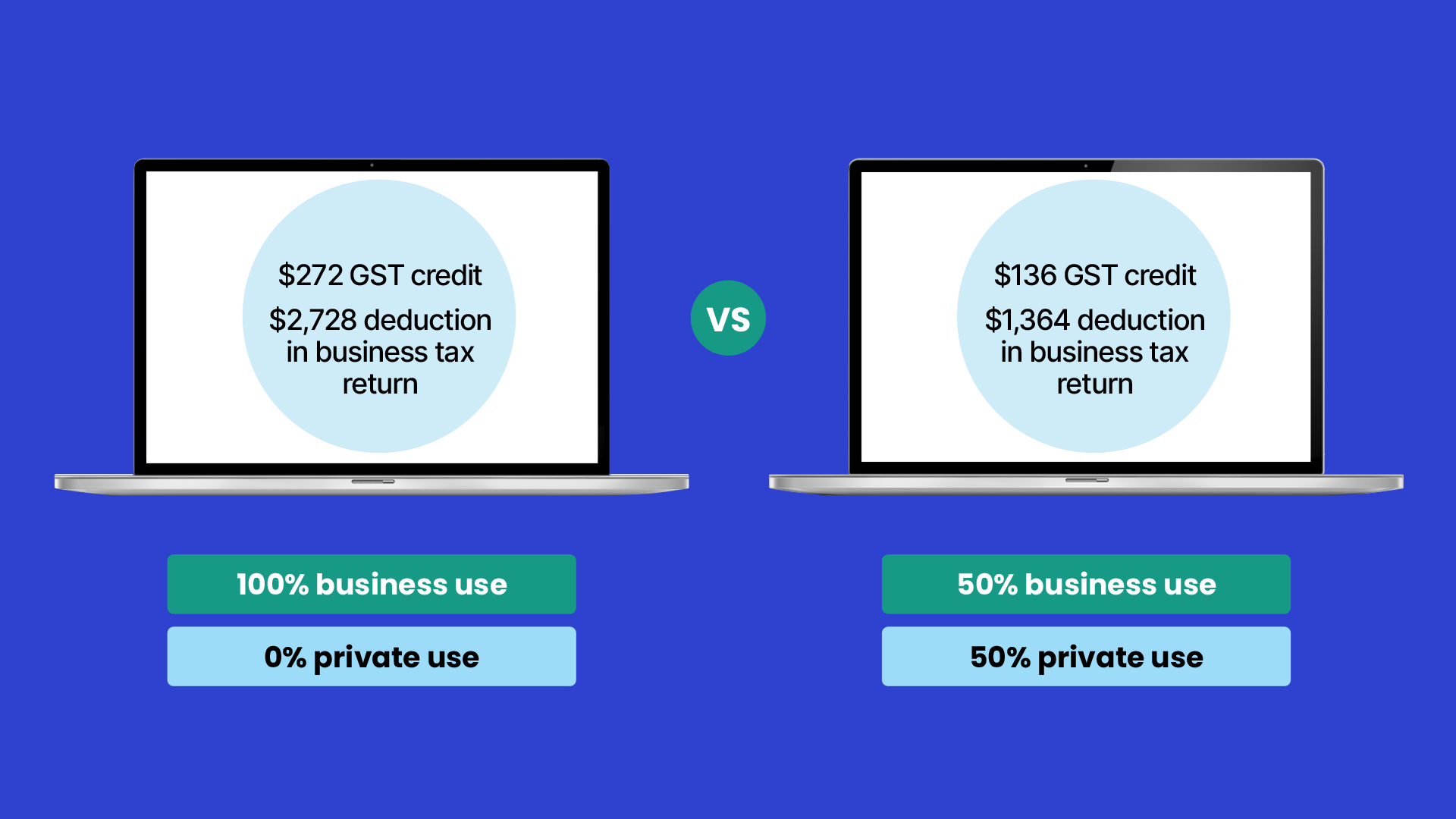
If you buy a $3,000 laptop which includes $272 GST, you can claim the GST credit of $272 in your business activity statement and the remaining $2,728 as a deduction in your business tax return.
If you’re going to use the laptop 50% for business and 50% for private use you can claim 50% of the GST credit which is $136 in your business activity statement and 50% of the remaining amount (which is $1,364) in your tax return. You cannot claim a GST credit for the portion used for private purposes.
If you have a business that is registered for GST, you have to apportion the GST credit, if you buy something that is for both business and private use.
Companies generally don’t apportion expenses for private use. If the company is paying for private expenses, fringe benefits tax (FBT) may apply instead.
Finally, if you use an item in your business for only part of a year you generally need to restrict your claim to the period it was used for the business.
Claiming small business tax deductions
| Steps | Progress | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
What are deductions and what can I claim? |
5 mins | |||||
Accounting for private use of assets |
9 mins | |||||
Expenses you can never deduct |
1 mins | |||||
Expenses you can deduct over time |
10 mins | |||||
Stock and asset records |
5 mins | |||||
Expenses you can deduct immediately |
5 mins | |||||
Other deductions records |
1 mins | |||||
Motor vehicle deductions |
4 mins | |||||
Motor vehicle deductions records |
2 mins | |||||
Related courses |
1 mins | |||||
Course feedback |
||||||
