
Occupancy expenses are what you pay to own, rent or use your home. They include:
- mortgage interest or rent
- council rates
- land taxes
- house insurance premiums.

The interest deductibility test
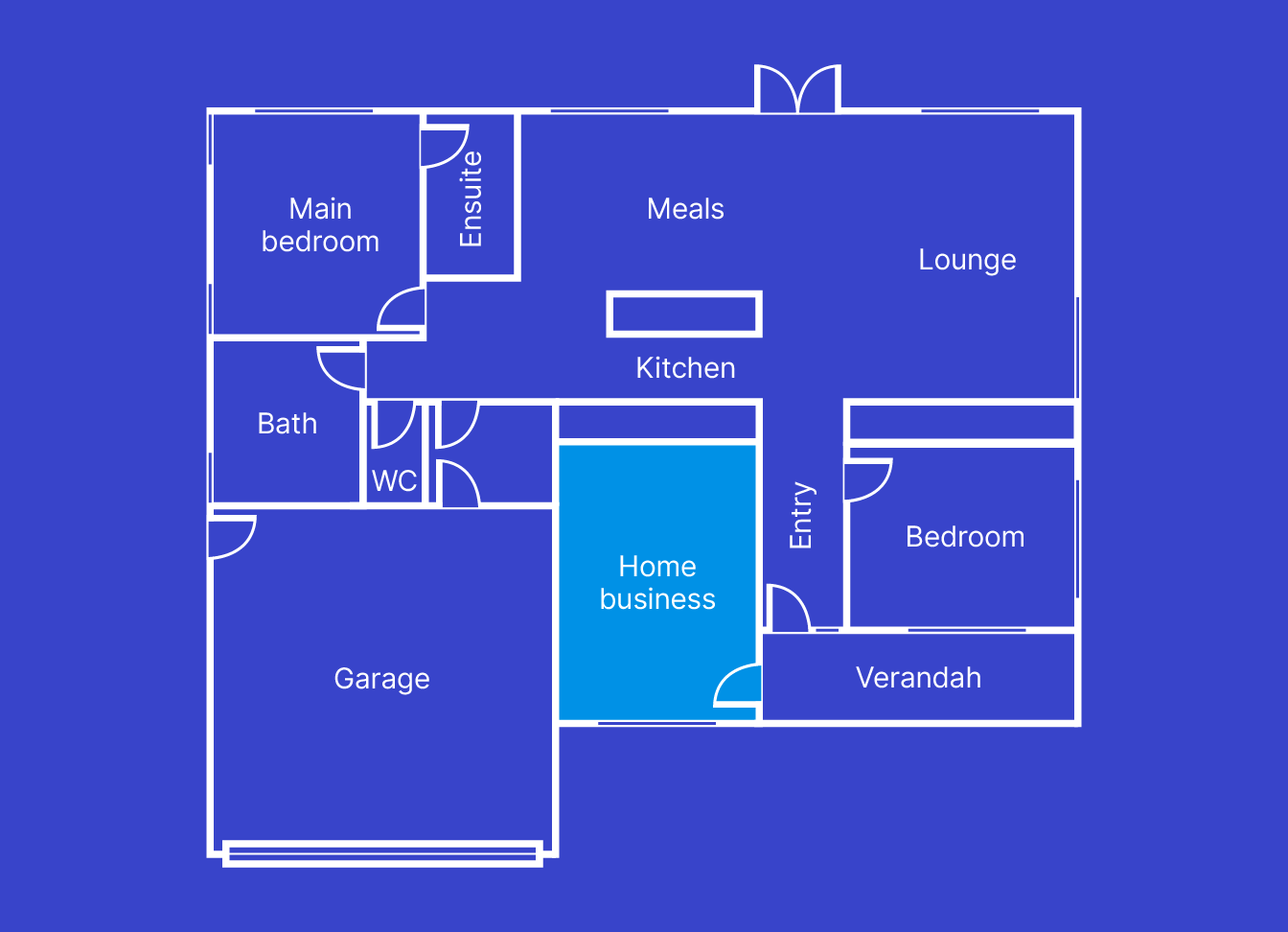
You can only claim occupancy expenses if you meet the interest deductibility test. You meet this test if the area of your house set aside for your business has the character of a ‘place of business’. This includes if most of your business is conducted online. Signs that the area of your home you’ve set aside is a place of business include:
- clearly identifiable as a place of business, for example, you have a sign identifying your business at the front of your house.
- not readily suitable or adaptable for private or domestic purposes.
- used exclusively or almost exclusively for carrying on your business.
- used regularly for visits by your clients or customers.
For example, a home hair salon business that is in the home but separate from the family living areas. There is also a dedicated entry for clients. This has the character of a place of business.
Paying tax on capital gains when you sell your home
If you pass the interest deductibility test, you may have to pay tax on any capital gains you make when you sell your home. This applies even if you didn't:
- borrow money to buy your home
- claim a deduction for mortgage interest as an occupancy expense.
When personal services income rules apply to your business
You may not be able to claim occupancy expenses if personal services income rules (PSI) apply to your business. To find out more, visit ato.gov.au/PSI.
Claiming deductions for your home-based business
| Steps | Progress | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
What is a home-based business? |
3 mins | |||||
Types of expenses |
7 mins | |||||
Calculating running expenses |
10 mins | |||||
Calculating occupancy expenses |
3 mins | |||||
How your business structure affects your deductions |
3 mins | |||||
Case studies: home-based business |
5 mins | |||||
Home-based business deductions records |
1 mins | |||||
Related courses |
1 mins | |||||
Course feedback |
||||||
