
You can use the floor area method if you have an area of your home set aside exclusively for business. That is, if this area of your home has the character of a place of business.
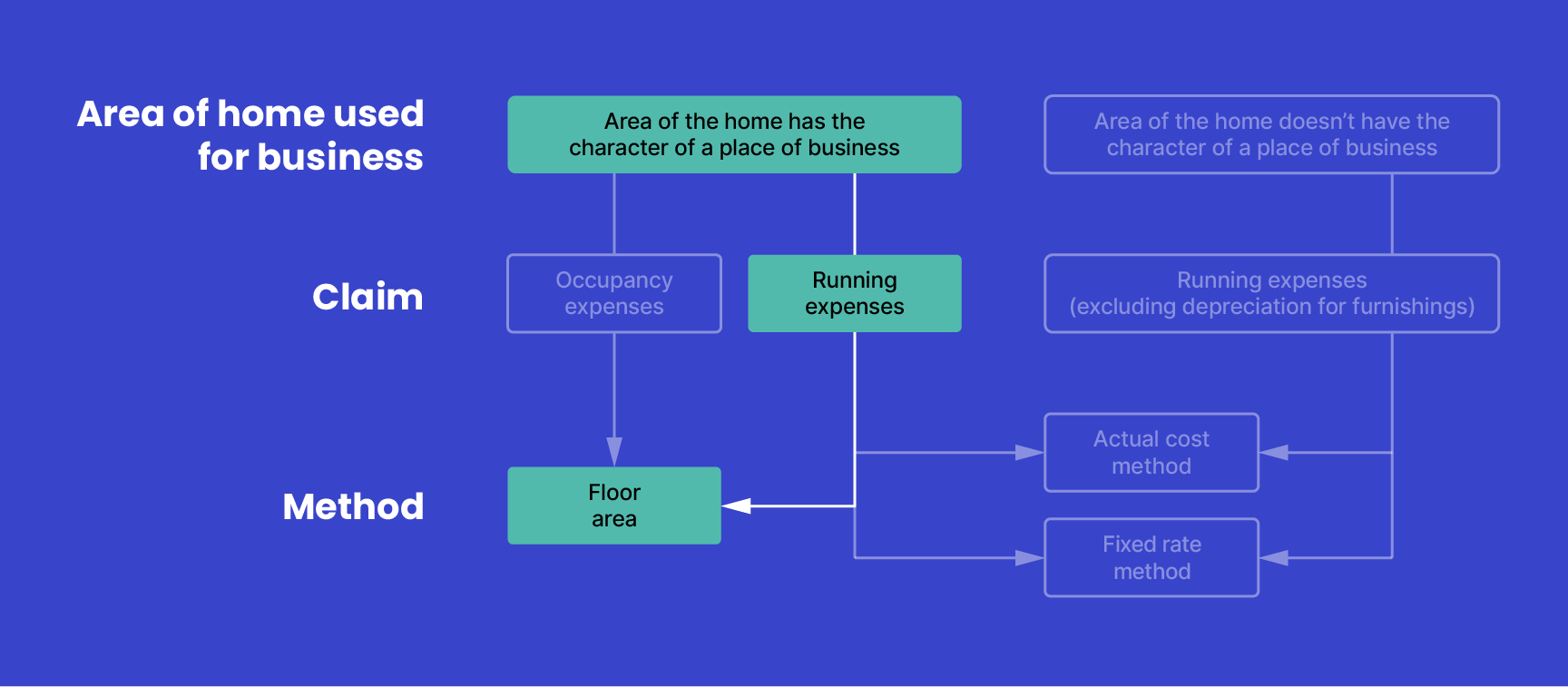
The actual amount which can be claimed is dependent on individual circumstances. In most cases using the floor area method to work out the portion of the total expense incurred is the most appropriate method.
For example, if the floor area of your home office is 10% of the total area of your home, you can claim 10% of your running expenses. In this case, the floor area method may be appropriate for expenses relating to:
- electricity
- gas
- cleaning.
If the business use percentage is based on anything other than the floor area (for example, on actual electricity use) you need to keep records, which show how you worked out the amount you are claiming.
How to calculate your claims
- Calculate the floor area that you use as your place of business – as a percentage of your entire home floor area
- Multiply the result by the relevant expenditure.
Formula: (Floor area for business use divided by Total floor area of home) x Relevant expenditure.
Example:
Annual electricity cost: $2,500
Area has the character of a place of business
(Floor area for business use divided by Total floor area of home) x Relevant expenditure
(10m2 divided by 560m2) x $2,500
= $44.64
In this example, $44.64 is the amount you can claim for the business portion of the annual electricity cost.
Claiming deductions for your home-based business
| Steps | Progress | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
What is a home-based business? |
3 mins | |||||
Types of expenses |
7 mins | |||||
Calculating running expenses |
10 mins | |||||
Calculating occupancy expenses |
3 mins | |||||
How your business structure affects your deductions |
3 mins | |||||
Case studies: home-based business |
5 mins | |||||
Home-based business deductions records |
1 mins | |||||
Related courses |
1 mins | |||||
Course feedback |
||||||
