
×
To use this feature, you need to log in to your account.
Don't have an account yet?
Create an account.
×
To use this feature, you need to log in to your account.
Don't have an account yet?
Create an account.
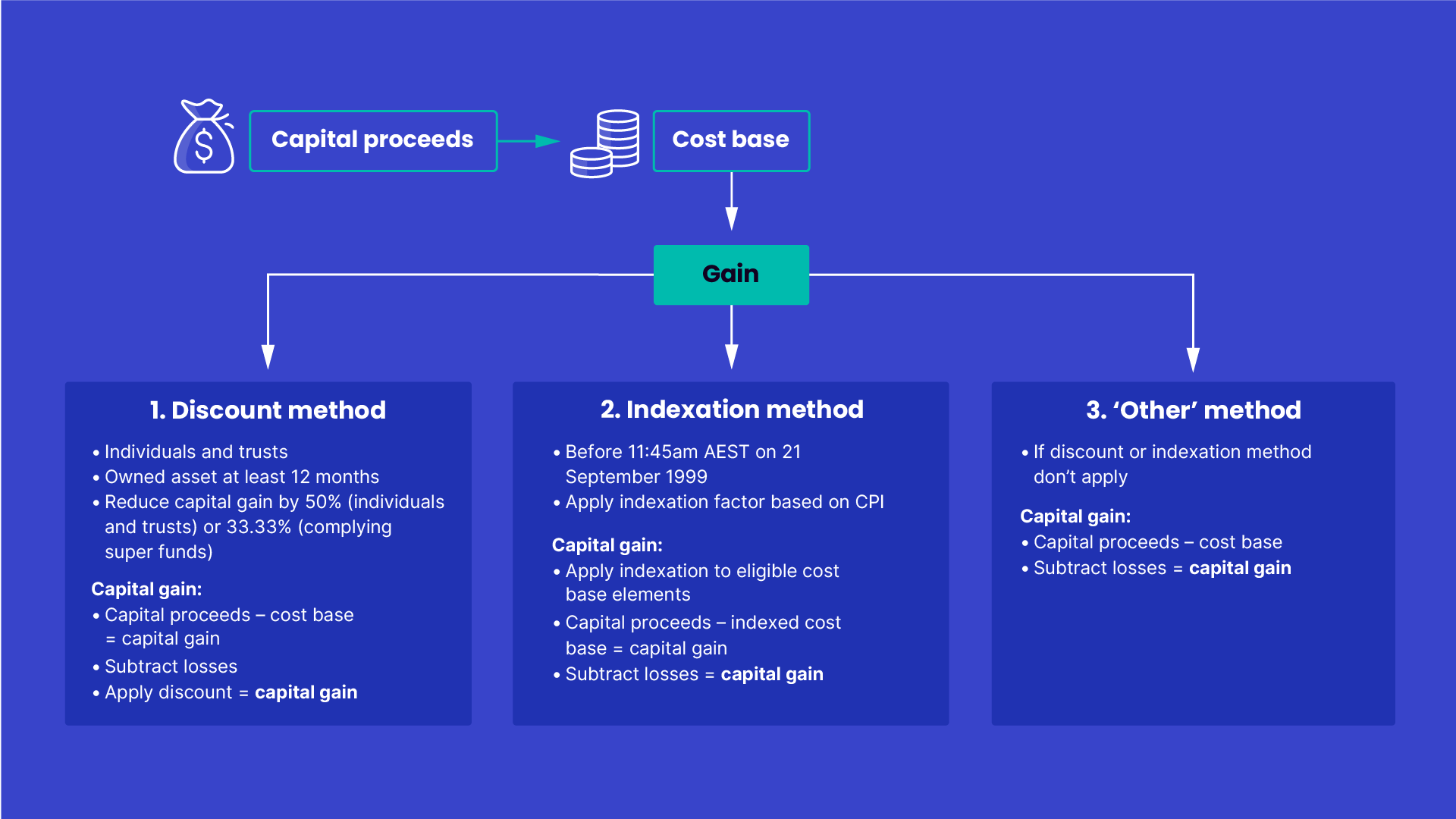
You must use the ‘other’ method when:
- the indexation and discount methods don’t apply, (for example, if you bought and sold an asset within 12 months), or
- for CGT events that don't involve an asset, such as the creation of a right (for example, entering an agreement to not start a similar business in an area for a period of time after you sell your business).
To calculate your net capital gain using this method, subtract the cost base (or the amount specified for the relevant CGT event) from the capital proceeds. Then subtract any unapplied current year capital losses or net capital losses from previous income years from the gain, to work out your capital gain.
Last modified: 16 Apr 2024
